Utility-scale PV system valuation: cost approach - financial audit checklist
PV monitoring in compliance with IEC 61724 standard “Class A” enables financial auditors and owners to claim the highest possible value of assets
When valuating PV assets, auditors may ask owners for both a “cost” - and an “income approach”. In both valuations the performance and degradation of the PV system play a large role. Performance is quantified using Performance Index (PI). Measuring PI with a higher accuracy results in:
higher PV asset valuation. Lower-risk, better bankability
earlier identification of underperformance and of hidden asset deterioration
prevention of unjustified value assessment (also in the special case of acceptance testing)
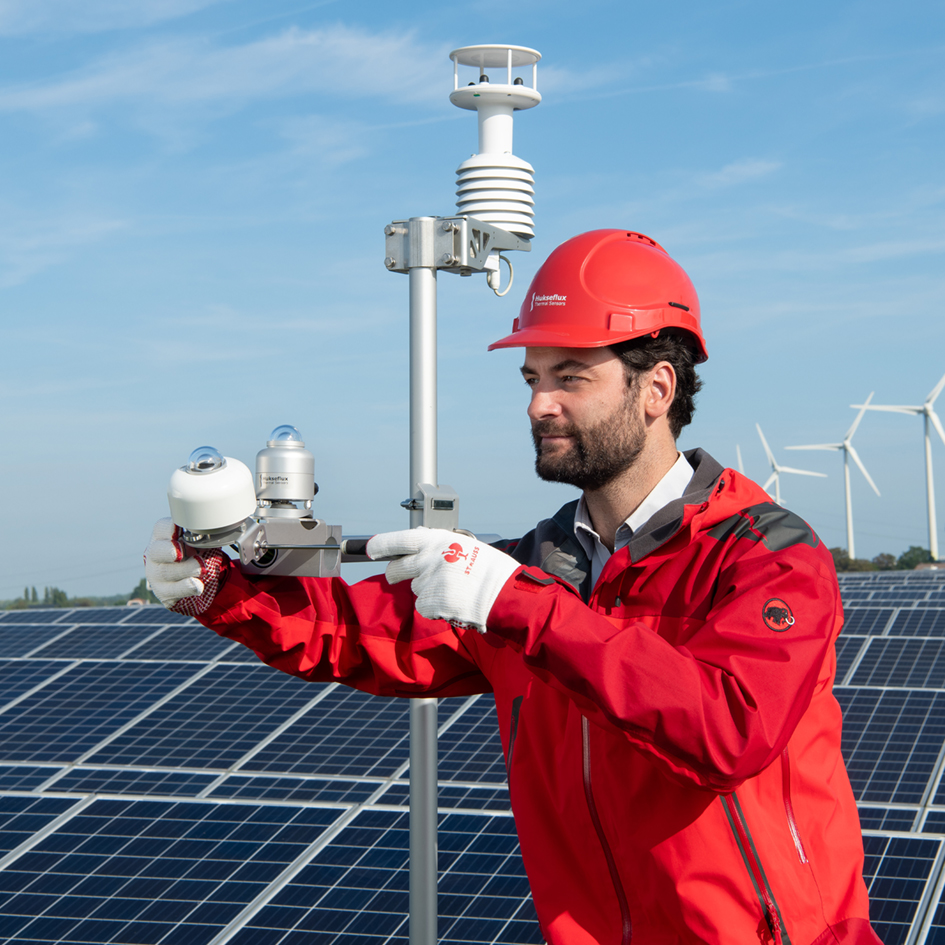
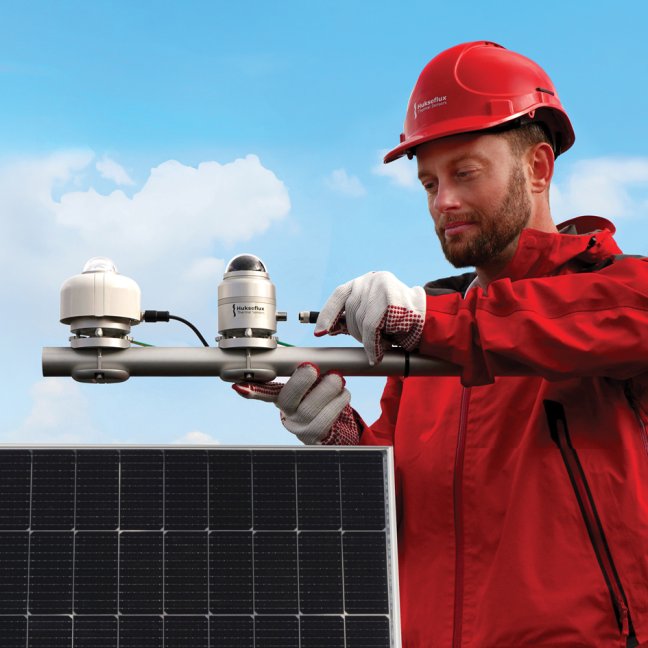
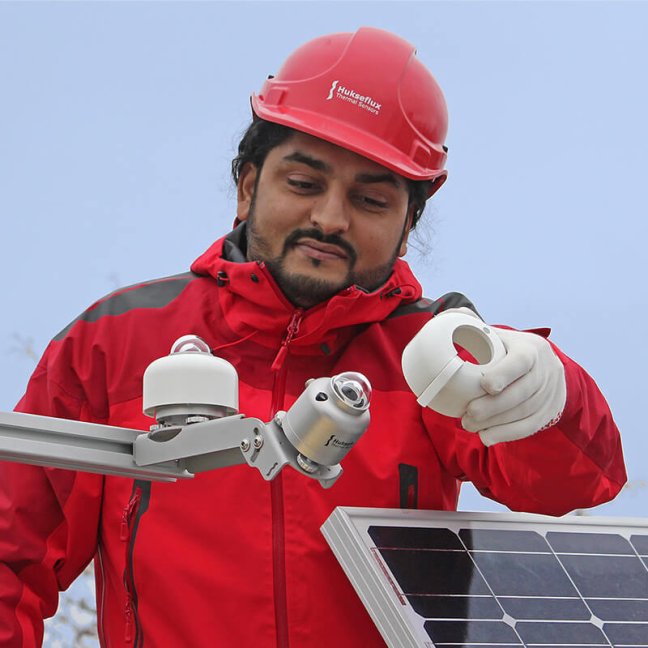
PI is measured by comparing incoming solar radiation to generated electrical output. Best practice is to do this in compliance with the latest IEC 61724 standards. However, many systems are still monitored according to the old (pre-2017) low-accuracy requirements of IEC. These qualify as “Class B”. If you want to benefit from new “Class A” accuracy, then your solar and electrical monitoring systems and their maintenance must comply with IEC’s requirements. This note explains how to get to the higher accuracy “Class A” and offers a checklist for financial auditors.
Read the full note here: Utility-scale PV system valuation: cost approach - financial audit checklist
Introduction
The IEC 61724 group of standards contains best practices for monitoring and reporting PV system performance. There is a general consensus that compliance with the latest version of the IEC standards results in the best accuracy data and best bankable reports.
In 2017 the IEC requirements for utility-scale PV system performance monitoring have changed significantly. However, many PV systems are still monitored according to the old (pre-2017) low-accuracy requirements of IEC
- since 2017, asset managers and their financial auditors aim for compliance with the high-accuracy “Class A “ requirements
- many O & M organisations still report data based on monitoring systems according to the pre-2017 IEC 61724 edition of 1998. These now qualify at best as “Class B”
- PV system owners can order new monitoring systems and their maintenance to Class A
- PV system owners can upgrade old monitoring systems and maintenance to Class A
This document explains the IEC 61724-1 standard for PV system performance, PV performance indicators, and provides a checklist to verify compliance of monitoring systems with the latest requirements of “IEC 61724-1 Class A”.
It aims to give objective information about the application of a standard. Comments are welcome at info@hukseflux.com
Performance indicators in PV
There are several performance indicators that form the basis of PV performance reporting and valuation of PV assets. The first edition of IEC 61724-1: Photovoltaic system performance monitoring – Guidelines for measurement, data exchange and analysis –, dates from 2008. It was the basis for the calculation of the main performance indicators for PV power plants:
- Performance Ratio (PR); this is the ratio of measured output to expected output for a given reporting period based on the system name-plate rating
- Performance Index (PI); this is the ratio of measured output to expected output for a given reporting period based on a more detailed model of system performance than the performance ratio
Why invest in high-accuracy monitoring?
High-accuracy monitoring adds value to asset management. For financial reporting, measuring PR and PI with a higher – Class A rather than Class B - accuracy results in:
- attribution of a higher value to the same asset, more favourable financing
- a lower-risk, better bankable valuation
- earlier identification of underperformance and of otherwise hidden asset deterioration
- prevention of unjustified value assessment
- improved directions for maintenance
Read the full note here: Utility-scale PV system valuation: cost approach - financial audit checklist